In February of 2018, MITH spent dedicated time talking about sustainability of digital projects with a team from the University of Pittsburgh’s Visual Media Workshop (VMW) as part of a focused user testing session for The Socio-Technical Sustainability Roadmap. The research project that produced the Roadmap was led by Alison Langmead, with Project Managers Aisling Quigley (2016-17) and Chelsea Gunn (2017-18). The final goal of that project was to create a digital sustainability roadmap for developers and curators of digital projects to follow. The work was initially based on what the project team discovered during its NEH-funded project, “Sustaining MedArt.” In this blog post, which is a late entry in MITH’s Digital Stewardship Series from 2016, I’m going to talk a bit about what I discovered during the process of using the roadmap for one of MITH’s projects, how I synthesized our discoveries in the form of a concrete tool for MITH to utilize the roadmap afterward, and how this has changed some of my conceptions about digital sustainability practices.
The process of walking a future digital project through the roadmap can be completed either in a full eight-hour day session, or two four-hour sessions. During the process, you work through three sections, each with different modules pertaining to aspects of a project’s future sustainability prospects. We chose the latter, with each attending member focusing on a different MITH project they were developing or working on. I opted to use a project for which we were awaiting funding at the time, Unlocking the Airwaves: Revitalizing an Early Public and Educational Radio Collection. Although significant time and effort went into developing the grant proposal for Airwaves, which included a section on sustainability, the Roadmap process cemented how much more concretely we could have been thinking through these issues, and how better planning for those components from the start would lead to better management of the project. In fact, one finding that Langmead and her team had discovered as they developed and tested the roadmap, is that thinking through the project management aspects of a digital project was a necessary first component to even being able to effectively get through the remaining sections of roadmap exercises. So as they went along, they added several elements and exercises to Sections A and B which force users to pinpoint the structural elements of their project. These include elements such as access points, deliverables, workflows, intellectual goals, data flow, and anticipated digital lifespan. This kind of work is essentially an extension of a project charter, which often includes a lot of these same basic concepts. In fact, Module B1 of the roadmap encourages users to create or reference existing charters, and stresses that using the roadmap in conjunction with a charter enhances the usefulness of both tools.
The lifespan questions in Section A were eye-opening, because although the need to ask them seems obvious – How long do you want your project to last? Why have you chosen this lifespan? – I think we as stewards of digital information feel compelled to predict unrealistically long lifespans, which Langmead and her collaborators define as “BookTime:”
“BookTime” is a term we have coined to denote a project lifespan equivalent to, “As long as a paper-based codex would last in the controlled, professional conditions of a library.” It may often be assumed that this is coterminous with “Forever,” but that belief relies heavily on a number of latent expectations about the nature of libraries, the inherent affordances of paper and glue, and other infrastructural dependencies.
The module asks us to acknowledge that not every digital project can realistically span decades into the future, and that sometimes this honesty is better for both the project and your team. The module also leverages concepts such as ‘graceful degradation,’ and ‘Bloom-and-Fade,’ both of which, in moments of dark humor, felt similar to planning for a project’s hospice care or estate. “It’s okay, everything dies, let’s just be open in talking about it and how we’ll get through it together.” Humor aside, it was a useful exercise for me to acknowledge that time, change, and entropy will stand in the way of a project achieving BookTime, and that that IS, in fact, okay.

The other two sections and exercises that I felt were the most useful and that provided the core, structural materials on which to base a sustainability plan were Sustainability Priorities (Section A4) and Technological Infrastructure (Sections B2 and B3). In the former, we were asked to list out the core structural components of a project “without which your project simply would not be your project,” and to list them in order of priority. This could include things such as, but not limited to, authority records, curated access points, facets, geo-spatial data, or digitized materials. We were also asked to define the communities that each property served. In the latter, we were asked to list out every single technological component of the project, from Google Drive, to Trello, to IIIF servers, to the university’s digital repository, define the function(s) of each, and assign project team members that are responsible for each. Then we were asked to realistically assess how long each technology was guaranteed to be funded, as well as “how the duration of the funding for members of your project team compares with the duration of the funding for technologies they maintain, keeping in mind that funding discrepancies may require special considerations and/or contingency plans to ensure uninterrupted attention.” Again, at first glance, much of this may seem very logical and obvious, but actually doing these exercises is illuminating (and sometimes sobering).
 After Sections A and B force you to have a reckoning with the deep dark potential (good and bad) of your project, Section C focuses on applying the the National Digital Stewardship Alliance (NDSA)’s Levels of Preservation to your identified structural components. The Levels of Preservation are a set of recommendations that align the entire the digital preservation spectrum in six core areas: Access, Backing up Work, Permissions, Metadata, File Formats, and Data Integrity. For each of these areas, the roadmap defines four ‘levels’ of commitment to each of these areas, and what each of those levels really mean. For example, Level 1 for Data Integrity involves designating which project members have credentials for certain accounts and services, and who has read/write/move/delete authorization. Levels 2-3 requires the ability to repair data and create fixity information for stable files, and Level 4 specifies the checking of that fixity data specifically in response to specific events or activities. After defining your current and anticipated levels in each area, you’re asked to define concrete actions your team would need to undertake in order to achieve your desired level. Once again, these exercises encourage expectation management, with comments like “Please note! Reaching Level 4 sustainability practices is not the goal. Your work here is to balance what your project needs with the resources (both in terms of technology and staff) that you have.” It also notes that it is “absolutely okay” to decide that your project will choose Level 0 for any one of these areas, choosing consciously not to engage with that area, using the resources you have to focus on what your team wants to prioritize.
After Sections A and B force you to have a reckoning with the deep dark potential (good and bad) of your project, Section C focuses on applying the the National Digital Stewardship Alliance (NDSA)’s Levels of Preservation to your identified structural components. The Levels of Preservation are a set of recommendations that align the entire the digital preservation spectrum in six core areas: Access, Backing up Work, Permissions, Metadata, File Formats, and Data Integrity. For each of these areas, the roadmap defines four ‘levels’ of commitment to each of these areas, and what each of those levels really mean. For example, Level 1 for Data Integrity involves designating which project members have credentials for certain accounts and services, and who has read/write/move/delete authorization. Levels 2-3 requires the ability to repair data and create fixity information for stable files, and Level 4 specifies the checking of that fixity data specifically in response to specific events or activities. After defining your current and anticipated levels in each area, you’re asked to define concrete actions your team would need to undertake in order to achieve your desired level. Once again, these exercises encourage expectation management, with comments like “Please note! Reaching Level 4 sustainability practices is not the goal. Your work here is to balance what your project needs with the resources (both in terms of technology and staff) that you have.” It also notes that it is “absolutely okay” to decide that your project will choose Level 0 for any one of these areas, choosing consciously not to engage with that area, using the resources you have to focus on what your team wants to prioritize.

Module A3 in written form
After the two four-hour meetings, my brain was full and I was full of new ideas about my project that probably should have already occurred to me, but that only coalesced in any meaningful way by walking through the roadmap process. I’ve also been around long enough to know that the giddy enthusiasm that comes after a meeting like this can die on the vine if those ideas aren’t transformed into actionable items and documented somewhere. I did have the printed roadmap modules and exercises with my written answers on them, and Langmead and her team were clear that if we wanted to merely file (or scan) those written documents and stop there, that was fine. But written in the final module of the roadmap is the recommendation that after its completion, “make sure that you store the documentation for this, and all other, STSR modules in one of your reliable sites of project documentation.” So after several months of contemplation, I finally determined that MITH’s most reliable current site of project documentation is Airtable, which we’ve been using more and more to track aspects of different projects.
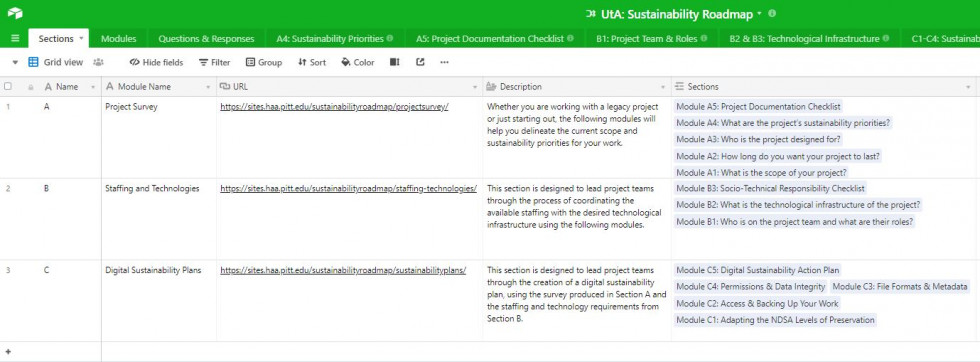
Airtable is an online relational database application that looks and functions like a spreadsheet in its default ‘Grid’ UI, but which also has more robust relational functions allowing you to meaningfully connect data between different tables/worksheets. As opposed to merely entering my answers to each module/exercise, I opted to begin by actually moving references and links to all the roadmap’s sections and modules into two tables in Airtable, so that the full text of each module was easily at hand for reference. I also included base, table, and
column descriptions at all levels (this would be the rough equivalent of Excel comments), which explain how information should be entered or that gave sample entries. The base description also provides an overview to this whole exercise, and gives attribution to the project in the format requested by Langmead and her team.
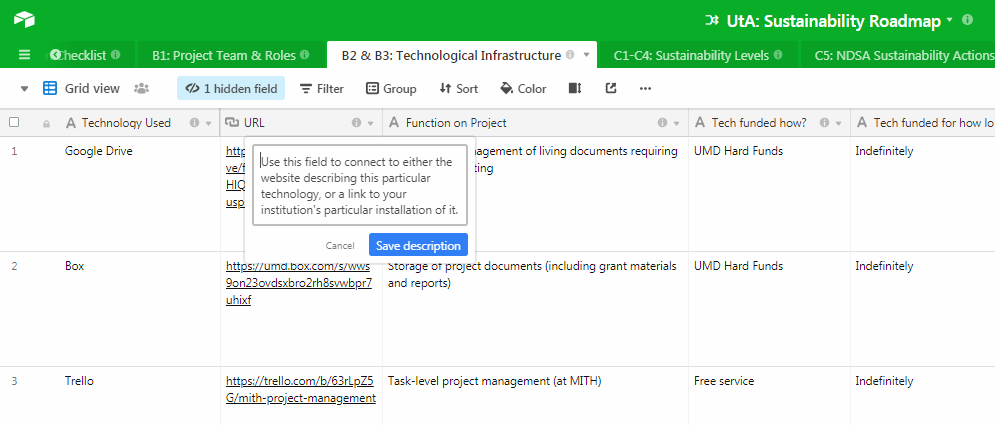
There are descriptions throughout with details on how to utilize each table or field. Click on the ‘i’ Info button to display them.
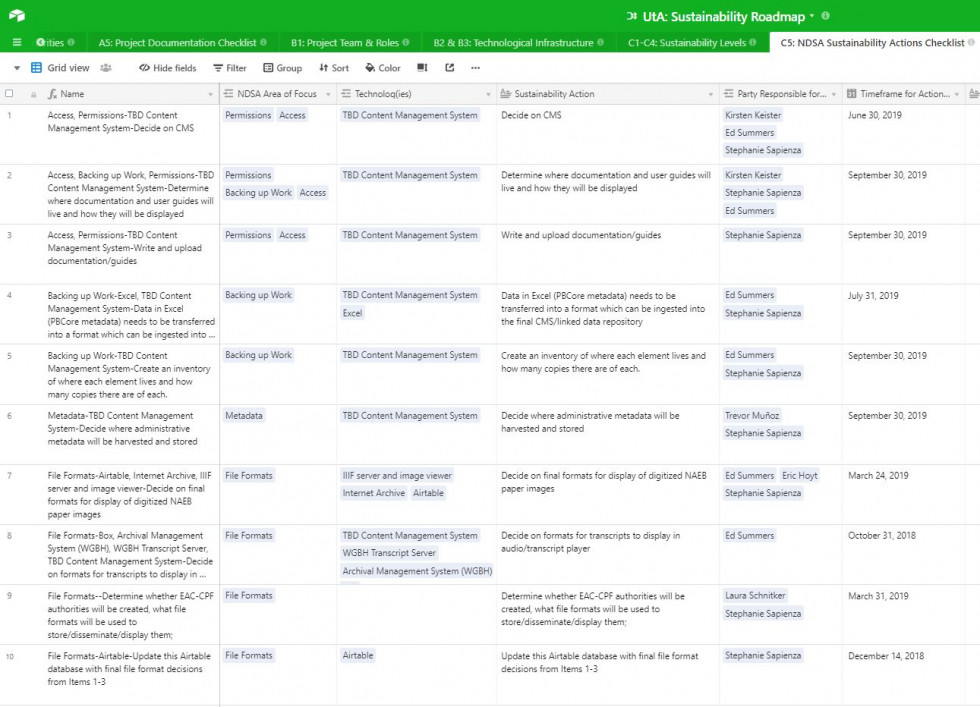
There were actual spreadsheets provided by the Roadmap’s project team for certain exercises, and I uploaded those as new tables in Airtable, and modified them as needed to connect/link with other tables. For example, the Technological Infrastructure table (which includes all the various technologies used by your project), the ‘Project Member Responsible’ column is linked to the Project Team table. So after you’ve entered the data for each, you can go back to the Project Team table and see all the tech components each member is responsible for, rolled up in a linked record field. There’s also a reference table listing out the definitions of Levels 1-4 for each of the six NDSA areas, so when you’re deciding what to enter in the Sustainability Levels table, you can instantly reference that table and choose an appropriate level for each area. After crafting the ‘template,’ I tested its usability by entering all the data from Unlocking the Airwaves that I’d written down. By doing that I realized where there were a few tweaks and bottlenecks that needed ironing out, and went back and modified the template. See below for a few more screenshots of the completed template.
So now we’ve got the roadmap data for Unlocking the Airwaves saved in a reliable site of project documentation. MITH team members are now encouraged (but not required) to use the template as we develop new projects, and it’s available to anyone else who’d like to request a blank duplicated copy. Dr. Langmead also provided a gentle but useful reminder that there is inherent risk in picking and using any such technology for this purpose, since platforms like Airtable may not always remain available. She suggested that we include a mention along the lines of “The inclusion of Airtable in your project’s suite of technologies should be considered carefully (in line with the work done in Modules A5 and B2)” in the intro description text for the base, which we did.
In a way this was also a sense-making exercise wherein, by taking all the roadmap data and turning it into structured data, I’d not only be able to sync up all these components in my head and turn them into actionable tasks, I’d also better retain the information. Anyone who has transformed, mapped, or structured previously unstructured data knows that by doing these tasks, you become much more intimately connected to your data. But what I think really appeals to me about the roadmap process is the mindfulness aspect. It encourages participants to think beyond the theoretical concepts of sustainability and actually apply them, write them down, look at them, consider their implications, and be honest about project expectations as aligned with available resources. In a world of overtapped resources and academic and bureaucratic hurdles, that’s an incredibly valuable skill to have.